How you can digitalize your business processes with Augmented and Virtual Reality
As logistics experts, we love digitalization processes that serve our value chain. But not all technical innovations meet our requirements and offer us real added value for our everyday work. We are currently exploring how the use of Augmented Reality or Virtual Reality in logistics can be evaluated. Top or Flop?
One thing in advance: It is worthwhile to deal with these technical assistants in a deeper way!
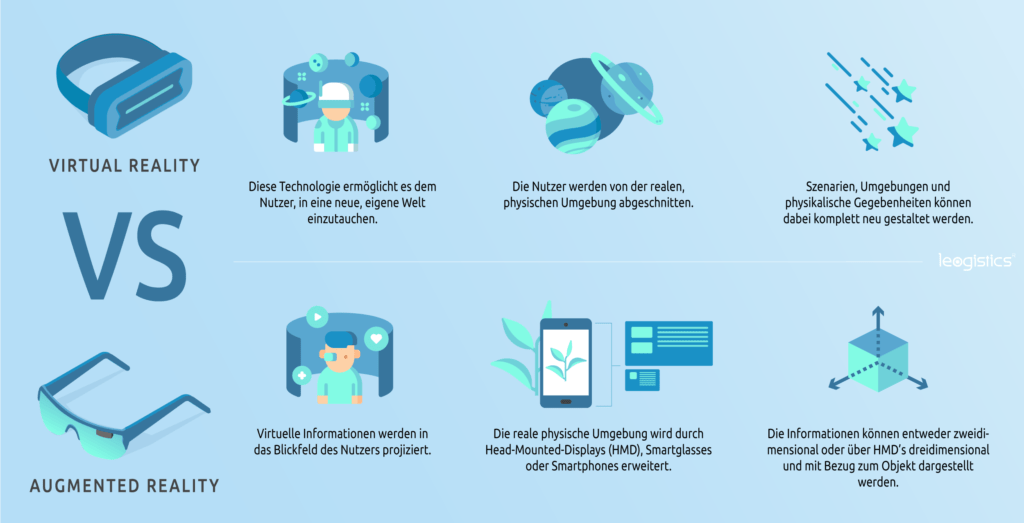
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) have reached a certain level of market maturity. Smart devices in the private sector are able to perform essential computing operations and display the content without any problems. App stores are filled with a very large number of possible applications. But what support does technological progress in the field of visualization bring to your logistics processes?

What exactly is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality or Assisted Reality is the extension of the perceived reality with the help of digital data. Here the real and the virtual world merge together. The projection of digital information into the real environment takes place interactively and always in real time with the help of technical equipment.
With Augmented Reality, physical and digital content can be processed simultaneously – in contrast to Virtual Reality where information is embedded in a fictional rather than a real environment.
Which problems can be tackled?
Many work processes on heavy equipment or in dangerous working environments require working with both hands. A tablet or scanner would hinder the work and pose an increased safety risk. New “wearables”, such as smart watches or glasses, can help here. Together with speech and gestures, meta-information can be called up and decisions implemented.
Augmented reality found its way into everyday life through apps such as Pokémon Go, IKEA and Snapchat. But it is also already present in other areas of our lives, without us noticing it directly, e.g. in the form of parking aids that assist us in our reality through images and sound (Assisted Reality).
Head-up displays in cars and airplanes are also a good example of Augmented Reality as an assistance assistant. Information such as navigation and other information is projected directly into the field of vision of the driver/pilot.
Currently, most AR apps are provided via mobile devices. Various application scenarios can be displayed using smartphone or tablet cameras. With the further development of Hands-Free Weareable Devices like Head-Mounted Displays and Smart Glasses.
Wherever the complexity of the work steps is very high, but no PC or notebook can be used for assistance due to physical peculiarities, a reality extension through Augmented Reality is sensible to employ.
What are the advantages of Augmented Reality?
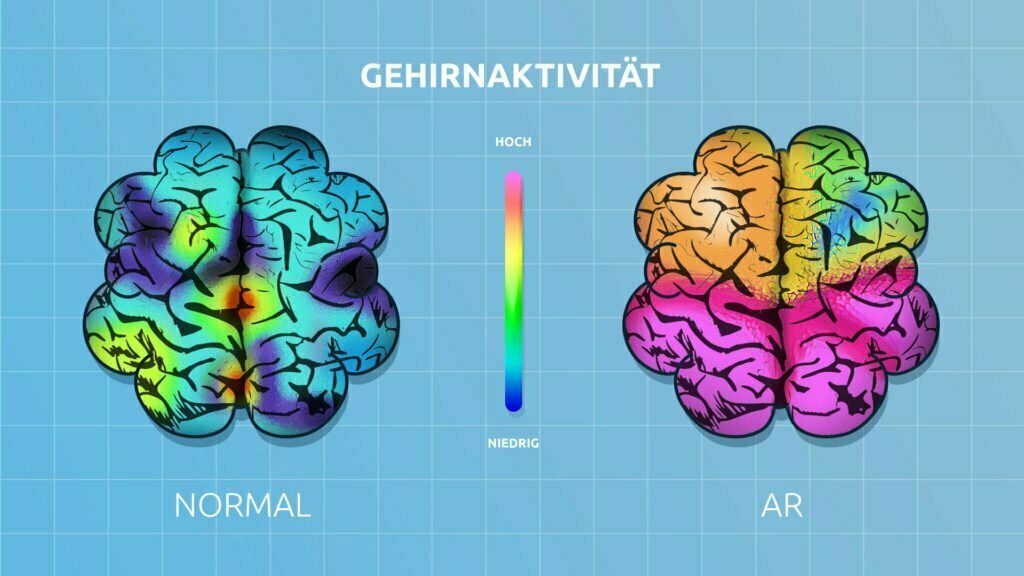
A study by Neuro-Insight revealed that during an AR experience, our brain showed almost twice as much cognitive function as its non-AR equivalent. This means that the brain is significantly more active during the study of a manual via augmented reality than when studying a manual in paper form.
Application: optimization of your load safety through AR-application
In the area of truck loading, good preparation of the freight is immensely important. Depending on the type of cargo, weight or route, there are requirements that must be met in order to ensure safe transport for people and materials. Loading is currently carried out on the basis of a loading list.
In most cases, the transport list does not provide the shipper with a visual assignment of where in the truck the freight should be secured. This can quickly lead to errors, which can cost important time for correction or lead to problems during unloading.
Loading assistance through visual assistants
By using augmented reality, the future positioning can be visually displayed to the shipper inside the truck. A head-mounted display can support the user without affecting his motor activities.

Use case: error reduction during equipment check (AR)
Safety and equipment checks are indispensable in logistics – be it when plant personnel check equipment to be transported or when safety-relevant components on a vehicle or machine are checked.
Such checklists can be supported very well by Augmented Reality. By projecting the checklists into the field of view, the user has a better overview. A virtual assignment to the physical object can also facilitate the processing of such a list.
Practical example: wagon detection with Augmented Reality
In the field of works railway logistics, leogistics has already been able to carry out initial tests with a head-mounted display. The correction of a track stock could be carried out in the near future with the help of augmented reality. The combination of augmented reality and voice control forms the basis for the hands-free acquisition and documentation of logistics processes.

Corrections in the track area can be made here with voice control. This represents an enormous relief for the employee in his work process, so that he can increasingly pursue his motor activities.
This technology can save a lot of time and, as a result, also a lot of money. Leogistics is constantly monitoring the technological progress of Head-Mounted Devices (HMD’s) in order to be able to implement Augmented Reality as soon as possible.
Augmented reality is primarily experienced via a head-mounted device, a portable wearable, or via a smartphone application.
Smartphone
Smartphones allow a quick entry into the AR world. Almost everyone owns an AR-enabled smartphone these days. Interactions are only possible handsfree to a limited extent and are generally still based on classic touch interactions on the display. Pioneers in the development of AR software technologies are Google and Apple.
HEAD-MOUNTED DEVICE: HOLOLENS 2, DAQRI
HMDs are devices that are worn like a helmet and enable the user to interact handsfree by means of gestures and speech. The pioneer here is Microsoft Hololens 2.
These all-in-one devices contain the necessary hardware directly on or near the helmet, are powerful and can be operated independently.
SMART GLASS: GOOGLE GLASS 2, VUZIX
Smart Glasses work similar to HMDs, but have a slimmer design and rely on an external device such as a smart phone. Smart Glasses are often lighter and easier to use, but are not suitable for complex visualizations due to the lack of hardware.
What the future holds and which technology will establish itself is still uncertain.
The tendency of the further development of hardware, especially for Smart Glasses and Head-Mounted Devices, shows that especially work processes from this environment benefit from the use of Augmented Reality.
What is your case of application?
Have you already dealt with application fields of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality? Could we spark your interest? Then please contact us.
Together we can examine your processes and check a possible support by visualization using Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality. We at leogistics build a prototype and test the application and process stability with you.
If you have any questions about this or other blog topics, please contact blog@leogistics.com.
Robert Ibisch
Jonas Falkenberg
Digital & Technical Consultants



